Innovation driving global competitiveness
In the rapidly evolving nutraceutical and superfood market, innovation has become the key differentiator that sets industry leaders apart. Blue spirulina, prized for its vibrant natural color and high phycocyanin content, represents a niche yet growing segment where research and development (R&D) plays a transformative role. In India, R&D initiatives are not only enhancing cultivation techniques and extraction efficiency but also enabling manufacturers to meet stringent global quality standards. By embracing scientific innovation, Indian blue spirulina producers are strengthening their competitiveness on the international stage, driving sustainable growth, and positioning India as a hub for high-quality, export-ready spirulina products.
For manufacturers in India, ensuring stability means that every batch of blue spirulina maintains consistent quality from production to the end consumer. A stable product guarantees that health claims are delivered reliably, shelf life is maximized, and customer trust is reinforced. In essence, stability isn’t just a technical specification—it defines product performance, efficacy, and market reputation.
Importance of R&D in Algae Industry
The algae industry has emerged as a cornerstone of the global nutraceutical, food, and biotechnology sectors, offering solutions ranging from superfoods to natural colorants and bioactive compounds. At the heart of this growth lies research and development (R&D), which fuels innovation, improves productivity, and ensures quality standards that meet international benchmarks. In a competitive global market, R&D enables companies to develop high-yield cultivation methods, optimize extraction processes, and create novel algae-based products with enhanced nutritional and functional properties. For countries like India, strategic investment in R&D not only strengthens domestic capabilities but also positions the nation as a global contender in algae production and exports. By harnessing scientific research and technological innovation, the algae industry can achieve sustainable growth, drive market differentiation, and remain at the forefront of global competitiveness.This sensitivity poses a significant challenge for manufacturers, as even minor deviations during processing, storage, or packaging can compromise the product’s quality. Understanding the natural vulnerabilities of phycocyanin is therefore critical for designing strategies that preserve its stability, ensure consistent product performance, and maximize shelf life. In the context of nutraceuticals, such as blue spirulina, private label manufacturing enables brands to offer high-quality, ready-to-market health ingredients without investing heavily in production facilities, research, or regulatory compliance. The manufacturer handles production, quality testing, and often packaging, while the brand owner controls the product’s identity, packaging design, and marketing strategy. From a regulatory standpoint, global food authorities are tightening norms around synthetic colors. Several artificial dyes face partial bans, warning label requirements, or usage restrictions across regions such as the European Union, the United Kingdom, and parts of Asia. In contrast, regulations continue to evolve, creating compliance challenges for food and beverage manufacturers that rely heavily on synthetic colorants. Constant monitoring, reformulation costs, and the risk of future bans make artificial colors a less sustainable long-term option. Blue spirulina manufacturers in India use standardized analytical methods, such as spectrophotometric absorbance ratios, to classify phycocyanin into different purity grades. Higher purity levels result in a more vibrant blue color, improved stability, and fewer impurities like chlorophyll or residual proteins. These factors are critical when phycocyanin is used in sensitive applications such as functional foods, nutraceuticals, cosmetics, and pharmaceuticals. Understanding phycocyanin purity helps buyers assess product quality, compare suppliers, and select the right grade based on intended use. Whether for natural food coloring or high-value health formulations, purity directly impacts performance, safety, and regulatory compliance.
Improving Extraction Yields
The efficiency of extracting phycocyanin—the blue pigment that defines blue spirulina—directly impacts both product quality and profitability. In India’s growing blue spirulina industry, research and development (R&D) plays a pivotal role in optimizing extraction methods, ensuring maximum yield while maintaining the purity and bioactivity of the pigment. Innovative approaches, such as advanced filtration techniques, enzymatic treatments, and sustainable solvent-free processes, are helping manufacturers overcome traditional limitations of low yields and high wastage. By focusing on these scientific advancements, Indian producers are not only improving operational efficiency but also elevating the global competitiveness of their products. Enhanced extraction yields mean higher-quality spirulina for domestic consumers and export markets alike, positioning India as a leader in high-value, nutraceutical-grade blue spirulina.

Enhancing Color Stability
One of the defining features of blue spirulina is its striking natural blue hue, derived from the pigment phycocyanin. For manufacturers, maintaining this vibrant color during processing, storage, and transport is critical, as it directly impacts product appeal, consumer trust, and market value. Through focused research and development, Indian producers are exploring innovative techniques—such as optimizing extraction methods, improving formulation stability, and leveraging natural preservatives—to enhance color retention without compromising nutritional benefits. By prioritizing color stability, R&D not only ensures superior product quality but also strengthens the global competitiveness of Indian blue spirulina in international nutraceutical and food markets.
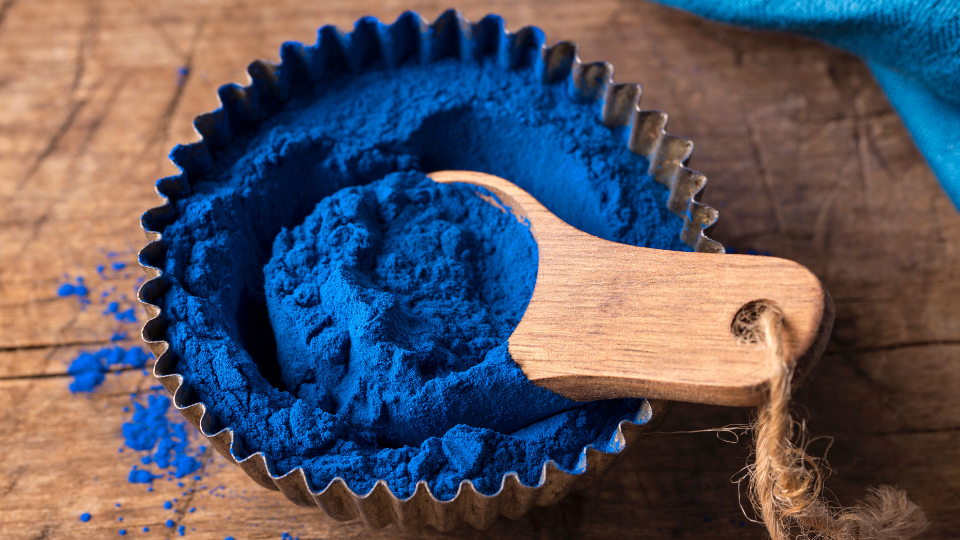

Developing New Formats
The versatility of blue spirulina goes far beyond traditional powders, opening up exciting opportunities for product innovation. Developing new formats—such as capsules, gummies, beverages, energy bars, and functional foods—allows manufacturers to cater to diverse consumer preferences while enhancing convenience and usability. In India, R&D efforts are pivotal in creating these novel formats, ensuring that the nutritional integrity, vibrant color, and bioactive compounds of blue spirulina are preserved. By exploring innovative delivery forms, Indian manufacturers can expand their domestic market reach, attract global consumers, and stay ahead in a competitive nutraceutical landscape.
Cost Reduction through Process Innovation
In the competitive world of blue spirulina manufacturing, controlling production costs without compromising quality is crucial for both domestic and international markets. Process innovation—refining cultivation methods, optimizing extraction techniques, and adopting automation—offers a powerful way to achieve this balance. By improving efficiency at every stage, from biomass growth to phycocyanin extraction, manufacturers can significantly reduce operational costs while enhancing product consistency and yield. In India, where the blue spirulina industry is rapidly expanding, such innovations not only strengthen profitability but also position companies to compete globally, delivering high-quality products at cost-effective prices.
Collaboration with Research Institutions
Collaboration with research institutions has become a cornerstone of innovation in blue spirulina manufacturing in India. By partnering with universities, biotechnology centers, and specialized research labs, manufacturers gain access to advanced cultivation techniques, cutting-edge extraction methods, and analytical tools for quality enhancement. These partnerships enable joint research on strain optimization, nutrient-rich growth media, and sustainable production practices, ensuring higher yields and consistent phycocyanin content.
Pilot Testing & Scale-Up
In blue spirulina manufacturing, moving from laboratory research to commercial production is a critical step that determines product quality, consistency, and market success. Pilot testing and scale-up processes bridge this gap, allowing manufacturers to validate cultivation methods, optimize extraction techniques, and ensure efficient resource utilization before full-scale production. In India, where the spirulina industry is rapidly expanding, strategic pilot testing enables producers to refine their processes, minimize risks, and maintain the high phycocyanin content that global buyers demand. By systematically scaling up operations, Indian manufacturers not only enhance productivity but also strengthen their position in the competitive international market, demonstrating that careful innovation and practical testing are the foundations of sustainable growth.
Intellectual Property Developments
In the competitive landscape of blue spirulina manufacturing, protecting innovations is just as important as creating them. Intellectual property (IP) developments, including patents, trademarks, and process copyrights, play a critical role in safeguarding novel cultivation methods, extraction technologies, and product formulations. For Indian manufacturers, a strong IP framework not only secures technological advancements but also enhances credibility in global markets, encouraging investment and collaboration. By strategically leveraging IP, companies can prevent imitation, boost commercial value, and maintain a competitive edge, ensuring that India remains at the forefront of cutting-edge blue spirulina innovation.
Future Research Directions
As the blue spirulina industry in India continues to grow, the role of research and development remains pivotal in shaping its future. Emerging research areas focus on optimizing cultivation systems to achieve higher phycocyanin yields while reducing production costs and environmental impact. Scientists are exploring advanced bioreactor designs, precision nutrient management, and automated monitoring systems to enhance both efficiency and product quality.